A cross sectional study to assess sleep quality in Type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: One of the commonest metabolic diseases is Diabetes mellitus. It is estimated that around 592 million people across the world would be living with diabetes by the year 2035. Multiple studies have recognized sleep disorder a novel risk factor for diabetes via peripheral neuropathy or endocrine metabolic pathway.
Objective: The present study was undertaken to assess the sleep quality in type 2 diabetic patients.
Methods: Thirty cases of controlled type II diabetes mellitus and thirty non-diabetic age matched controls, including both males and females, were assessed for sleep quality. Sleep quality was assessed by Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI).
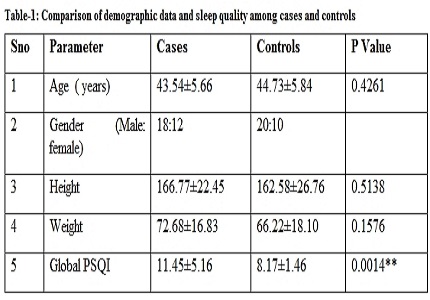
Results: Demographic data was not significantly different between cases and controls. Sleep quality was significantly lower in cases when compared to controls (P<0.01).
Conclusion: We have observed decrease in the quality of sleep in patients of diabetes. We recommend further studies to explore the association for planning and developing better treatment procedures.
Downloads
References
2. Gupta R, Misra A. Type 2 diabetes in India: Regional disparities. Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 2007; 7 (1):12-6.
3. Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C. Current scenario of diabetes in India. J Diabetes. 2009 Mar;1(1):18-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-0407.2008.00004.x. Epub 2008 Dec 17.
4. Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, Ohinmaa A, Pajunpaa H, Koivukangas P: Health related quality of life in diabetic patients measured by the Nottingham Health Pro- file. Diabet Med.1996; 13:382–388.
5. Resnick HE, Redline S, Shahar E, Gilpin A, Newman A, Walter R, Ewy GA, Howard BV, Punjabi NM; Sleep Heart Health Study. Diabetes and sleep disturbances: findings from the Sleep Heart Health Study. Diabetes Care. 2003 Mar;26(3):702-9. [PubMed]
6. Barone MT, Menna-Barreto L. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011 Feb;91(2):129-37. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2010.07.011.
7. Spiegel K, Knutson K, Leproult R, Tasali E, Van Cauter E. Sleep loss: a novel risk factor for insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005 Nov;99(5):2008-19. [PubMed]
8. Kawakami N, Takatsuka N, Shimizu H. Sleep disturbance and onset of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004 Jan;27(1):282-3. [PubMed]
9. Resnick HE, Redline S, Shahar E, Gilpin A, Newman A, Walter R, Ewy GA, Howard BV, Punjabi NM; Sleep Heart Health Study. Diabetes and sleep disturbances: findings from the Sleep Heart Health Study. Diabetes Care. 2003 Mar;26(3):702-9. [PubMed]
10. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989 May;28(2):193-213. [PubMed]
11. Upadhyay RP. An overview of the burden of non-communicable diseases in India.Iran J Public Health. 2012;41(3):1-8. Epub 2012 Mar 31. [PubMed]
12. International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes atlas 5th edition. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels.2013.
13. Hayashino Y, Fukuhara S, Suzukamo Y, Okamura T, Tanaka T, Ueshima H; HIPOP-OHP Research group. Relation between sleep quality and quantity, quality of life, and risk of developing diabetes in healthy workers in Japan: the High-risk and Population Strategy for Occupational Health Promotion (HIPOP-OHP) Study.BMC Public Health. 2007 Jun 28;7:129.
14. Lou P, Qin Y, Zhang P, Chen P, Zhang L, Chang G, Li T, Qiao C, Zhang N. Association of sleep quality and quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study in China.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015 Jan;107(1):69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.09.060. Epub 2014 Oct 17.
15. Shankar A, Syamala S, Kalidindi S. Insufficient rest or sleep and its relation to cardiovascular disease, diabetes and obesity in a national, multiethnic sample.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 30;5(11):e14189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014189.
16. Resnick HE Diabetes and sleep disturbances: findings from the Sleep Heart Health Study.Diabetes Care. 2003 Mar;26(3):702-9., Redline S, Shahar E, Gilpin A, Newman A, Walter R, Ewy GA, Howard BV, Punjabi NM; Sleep Heart Health Study.
17. Almeida GPL, Lopes HF. Síndrome metabólica e distúrbios do sono. Rev Soc Cardiol São Paulo 2004 abril; 14(3):140.
18. Geib LTC, Cataldo A Neto Neto, Wainberg R, Nunes ML. Sono e envelhecimento. Rev. Psiquiatr Bras 2003 setembro; 25(3):453-65.
Copyright (c) 2017 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

