Diagnostic flexible fiber optic laryngoscopy and 70-degree hopkins rod lens laryngoscopic study in patient with hoarseness and dysphagia: a comparative study
Abstract
Objectives: To use Flexible Fiber Optic Laryngoscopy and 70-degree Hopkins Rod Lens Laryngoscope in diagnosis of patient with Hoarseness and Dysphagia.
Introduction: Laryngoscopy is examination or visualization of laryngeal structures which can be Endoscopes or rigid Laryngoscopy. Endoscopic and Fiber Optic laryngoscope is usually done under local anaesthesia in adults and general anaesthesia in children. Earlier pharyngeal and laryngeal pathologies required hospitalization for examination and procedure with rigid laryngoscopy under general anaesthesia but when Endoscopic laryngoscopy and Fibre Optic laryngoscope come in use these procedures can be done under local anaesthesia in OPD basis which decrease not only patients and doctors valuable time but also economic burden.
Materials and methods: Study was conducted in Department of ENT from August 2017 to August 2019 in Amaltas Institute of Medical Sciences, Dewas, Madhya Pradesh. Total 309patients were taken with age group of 10 to 60 who presented with symptoms of hoarseness and Dysphagia. Detailed clinical examination done for odynophagia, difficulty in breathing and cervical lymph nodes. Initially Endoscopic 70-degree Hopkins Rod Lens done under local anaesthesia and findings are compared with that of Flexible Fiberoptic laryngoscopy under local anaesthesia.
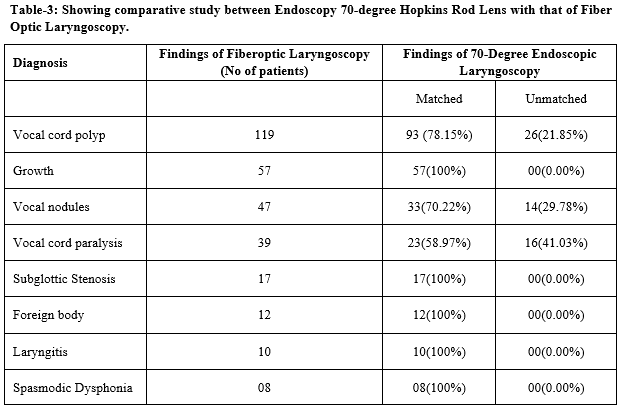
Conclusion: Flexible Fiber Optic laryngoscopy is an important tool for detailed examination of nasopharynx and larynx. Endoscopic laryngoscopy70 degree Hopkins Rod Lens is quick & easy OPD procedure for examination of Larynx.
Downloads
References
Garcia M. Observation on human voice. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 1855;7:397-410. doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rspl.1854.0094.
Bozzini P. The light guide or description of a simple device, and its application for illuminating inner cavities, and spaces of the living anima mesh body. Weimar, 1807
Kleinsasser O. Restoration of the voice in benign lesions of the vocal folds by endolaryngeal microsurgery. J Voice. 1991;5:257-263.
Hirschowitz B. A fibreoptic flexible esophagoscope. JAMA, 1963; 2:388.
Sawashima M, Hirose H. New laryngoscopic technique by use of fibre optics. J Acoust Soc Am. 1968;43(1): 168-169. doi: https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1910752.
Charlin B, Brazeau-Lamontagne L, Guerrier B, Leduc C. Assessment of laryngeal cancer: CT scan versus endoscopy. J Otolaryngol. 1989;18(6):283-288.
Kerr A., ed Scott-Brown’s Otolaryngology 1996, Vol 5, 6thedn. Butterworth Heinemann, London.
Choy AT, gluckman PG, Tong MC, Van Hasselt CA. Flexible nasopharyngoscopy for fish bone removal from the pharynx. J Laryngol Otol, 1992:106(8):709-711. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/s002221510012064x.
Barker M, Dort JC. Laryngeal examination: a comparison of mirror examination with a rigid lens system, J Laryngol Otol, 1991;20(2):100-103.
Pott LM, Murray WB. Review of video laryngoscopy and rigid fiberoptic laryngoscopy. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008;21(6):750-758. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0b013e3283184227.
Monnery PM, smith WK, Hinton HE. Laryngoscopy findings in outpatient notes: the accuracy of the recording of the side of the lesion. Clin Otolaryngol, 2001;26(4):278-280. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2273.2001.00460.x.
Bastian R.W. Benign vocal fold mucosal disorders. In: Paul W. flint, Bruce H. Haughey, Valerie J. Lund et al, editors. Cummings Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 5th Edn. Philadelphia: Mosby; 2010. P. 859-882.
Brodnitz FS. Goals, Results and limitation of vocal rehabilitation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1963;77(2):148. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.77.2.44.
Sataloff R.T., Spiegel J.R., Hawkshaw M.J. Strobovideolaryngoscopy: Results and clinical value. Annals Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1991;100(9 pt 1):725-727. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949110000907.
Casiano R.R., Vijaykumar Z., Lundy D.S. Efficacy of videostroboscopy in the diagnosis of voice disorders. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992;107(1):95-100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989210700115.
Woo P., Colton R., Casper J., Brewer D. Diagnostic value of stroboscopic examination in hoarse patients. J Voice. 1991;5(3):231-238. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-1997(05)80191-2.
Merati A.L. Acute and chronic laryngitis. In: Paul W. flint, Bruce H. Haughey, Valerie J. Lund et al, editors. Cummings Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 5th Ed. Philadelphia: Mosby; 2010. P. 883-888.
Jeannon J.P., Macnamara M. Assessment and examination of the upper respiratory tract. In: Michael Gleeson, George G browning, Martin J Burton et al. editors. Scott–Brwon's Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery 7th Edn. London: Hodder Arnold; 2008. P. 2145 – 54.
Rammage L., Morrison M., Nichol H. Management of the Voice and Its Disorders. 2nd ed. San Diego, Singular Publishing Group, 2001.
Hirano M., Bless D.M. Videostroboscopic Examination of the Larynx. San Diego, Singular Publishing Group, 1993.
Izdebski K, Ross JC, Klein JC. Transoral rigid laryngovideostroboscopy (phonoscopy). In Seminars in Speech Lang. 1990;11(1):16-26.
Johnson PE, Belafsky PC, Postma GN. Topical nasal anesthesia for transoral fiberoptic laryngoscopy: a prospective, double – blind, cross over study. Otolaryngol Head and Neck Surg. 2003;128(4):452-454. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0194-5998(02)23294-5.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

