A descriptive study comparing the surgical outcomes between power-assisted adenoidectomy and conventional surgical methods
Abstract
Objective:To study the surgical outcomes between power assisted and conventional curettage adenoidectomy.And to perform retrospective analysis by comparing the two surgical methods on the basis of duration of surgery, intra-operative blood loss, postoperative complications like bleeding and associated trauma.
Design:A retrospective and prospective study of 100 cases was performed in a tertiary care teaching hospital in Mumbai. Over 1 year and 8 months. The mean operative time was faster in conventional method (p<0.0001). Subjects:100 cases.
Methods: After selection of cases retrospective assessment of peri-operative conditions were obtained from case records duration of surgery, Intraoperative blood loss, Postoperative complications. The same cases were called for prospective analysis data on long-term postoperative outcome was obtained by using ‘Paediatric Throat Disorders Outcome Test’
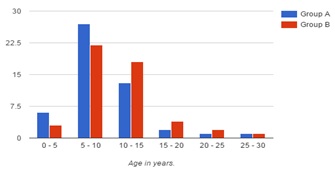
Result:Our 100 patients ranged from 4 to 27 years with mean age of 10.43 years with SD of 4.24 F : M ratio was 1.17. The operative blood loss between two groups was not statistically significant (p=0.4901). The symptomatic relief after conventional surgery and power assisted method was statistically significant (p < 0.0001). There was no statistical significance between outcomes of both methods.
Conclusions: Our study shows that the power assisted adenoidectomy was a safe, well tolerated procedure and an useful tool for adenoidectomy with disadvantages of high cost. Conventional adenoidectomy with a curette is safe, fast and economical. It fails to obtain complete tissue removal and thus is less effective than the power assisted techniques.
Downloads
References
2. Scadding G. Non-surgical treatment of adenoidal hypertrophy: the role of treating IgE-mediated inflammation. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010 Dec;21(8):1095-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2010.01012.x.[pubmed]
3. Robb Peter J .Scott-Brown's Otorhinolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7thEd :CRC Press; 2008:1094–1101.
4. Cannon CR, Replogle WH, Schenk MP. Endoscopic-assisted adenoidectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999 Dec;121(6):740-4.[pubmed]
5. Hopkins C, Fairley J, Yung M, Hore I, Balasubramaniam S, Haggard M. The 14-item Paediatric Throat Disorders Outcome Test: a valid, sensitive, reliable, parent-reported outcome measure for paediatric throat disorders. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology. 2010 Mar;124(3):306-14.
6. Parikh SR, Coronel M, Lee JJ, et al. Validation of a new grading system for endoscopic examination of adenoid hypertrophy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006 Nov;135(5):684-7.[pubmed]
7. Thomson S. Recurrence Of Adenoids And Tonsils. British Medical Journal. 1917;2(2960):400-401.
8. Pagella F, De Amici M, Pusateri A, et al. Adenoids and clinical symptoms: Epidemiology of a cohort of 795 pediatric patients. Int J PediatrOtorhinolaryngol. 2015 Dec;79(12):2137-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.09.035. Epub 2015 Oct 8.[pubmed]
9. Rout MR, Mohanty D, Vijaylaxmi Y, et al. Adenoid Hypertrophy in Adults: A case Series. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Jul;65(3):269-74. doi: 10.1007/s12070-012-0549-y. Epub 2012 Mar 29.[pubmed]
10. Al-Mazrou, KA; Al-Qahtani, A & Al-Fayez AI. (2009). Effectiveness of transnasal endoscopic powered adenoidectomy in patients with choanal adenoids. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.73, No.12, pp. 1650-1652.
11. Havas T, Lowinger D. Obstructive adenoid tissue: an indication for powered-shaver adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002 Jul;128(7):789-91.[pubmed]
12. Koltai PJ, Kalathia AS, Stanislaw P, et al. Power-assisted adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997 Jul;123(7):685-8.[pubmed]
13. Rodriguez, K; Murray, N &Guarisco, JL. Power-assisted partial adenoidectomy. Laryngoscope,2002;112:(8) Pt.2 Suppl.100, pp. 26-28.
14. Datta R, Singh VP, Deshpal. Conventional Versus Endoscopic Powered Adenoidectomy: A Comparative Study. Med J Armed Forces India. 2009 Oct;65(4):308-12. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(09)80089-0. Epub 2011 Jul 21.[pubmed]
15. Bradoo, Renuka A., et al. Comparison of Endoscopic-Assisted Adenoidectomy with Conventional Method. An International Journal Clinical Rhinology 4.2 (2011): 75-78.
16. Feng Y, Yin S. [Comparison of the powered-assisted adenoidectomy with adenoid curette adenoidectomy]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Jan;20(2):54-7.[pubmed]
17. Stanislaw P Jr, Koltai PJ, Feustel PJ. Comparison of power-assisted adenoidectomy vs adenoid curette adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000 Jul;126(7):845-9.[pubmed]
18. Vokurka J. Shaver (micro debridor) in otorhinolaryngology. International Congress Series. 2003;1240:1411–15.
19. Inancli HM, Enoz M. Odds and evens for endoscopic adenoidectomy. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2009 Feb;29(1):51; author reply 51-2.[pubmed]
20. Elluru, RG, Johnson L, Myer CM. Electrocautery adenoidectomy compared with curettage and power-assisted methods. Laryngoscope, 2002;Vol.112, No.8 Pt. 2 Suppl.100, pp. 23-25.[pubmed]
21. Ark N, Kurtaran H, Ugur KS, et al. Comparison of adenoidectomy methods: examining with digital palpation vs. visualizing the placement of the curette. Int J PediatrOtorhinolaryngol. 2010 Jun;74(6):649-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.03.012. Epub 2010 Apr 3.[pubmed]
22. Costantini F, Salamanca F, Amaina T, Zibordi F. Videoendoscopic adenoidectomy with microdebrider. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2008;28:26–9.[pubmed]
23. Öztürk Ö, Polat Ş. Comparison of transoral power-assisted endoscopic adenoidectomy to curettage adenoidectomy. Adv Ther. 2012 Aug;29(8):708-21. doi: 10.1007/s12325-012-0036-6. Epub 2012 Jul 31.[pubmed]
24. Kemaloglu YK, Goksu N, Inal E, et al. Radiographic evaluation of children with nasopharyngeal obstruction due to the adenoid. Ann OtolRhinolLaryngol. 1999 Jan;108(1):67-72.[pubmed]
25. Havas T, Lowinger D. Obstructive adenoid tissue: an indication for powered-shaver adenoidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002 Jul;128(7):789-91.[pubmed]
26. Gillespie, M. B., Ingram, F., Scarlett, M., & Hoy, M. Value-based approach to power-assisted adenoidectomy. Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology 2003; 112(7), 606-610.
Copyright (c) 2019 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

