Benign peroxismal positional vertigo: our experience in 40 cases
Abstract
Introduction: BPPV is the most common cause of vertigo provoked by certain head position changes. Despite being the most common cause of peripheral vertigo, BPPV is still often misdiagnosed hence it is important to understand BPPV not only because it may avert expensive and often unnecessary investigations, but also because treatment by particle reposition maneuvers is rapid, easy and effective in more than 90% of cases.
Objectives: 1) To analyze the etiological, clinical and prognostic differences between patients affected by BPPV. 2) To evaluate the efficacy of different PRM in the treatment of BPPV and to compare the results of present study with similar studies done elsewhere.
Methods: The present descriptive study was conducted at Department of ENT, Subbaiah institute of medical sciences, Shimoga from August 2015 to August 2018 in 40 patients with a clinical diagnosis of BPPV. All these patients were treated by different PRM specific for the canal involved and the results were analyzed.
Results: Right labyrinth was involved in 23 cases (57.5%) and left in 17 (42.5%) cases. PC was involved in 34 (85%) cases and Eply’s maneuver was successful in all 34 (100%) patients. HC was involved in 6 (15%) cases which were treated with Barbecue and Gufoni maneuver with resolution in 5 (83.33%) patients.
Conclusion: Therapeutic maneuvers are effective in treatment of BPPV that have shown high success rate hence should be tried in all patients with BPPV unless contraindicated to reduce unnecessary diagnostic tests and costs.
Downloads
References
2. van der Zaag-Loonen HJ, van Leeuwen RB, et al. Prevalence of unrecognized benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in older patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Jun;272(6):1521-4. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3409-4. Epub 2014 Dec 9.[pubmed]
3. von Brevern M, Seelig T, Neuhauser H, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo predominantly affects the right labyrinth. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004 Oct;75(10):1487-8. DOI:10.1136/jnnp.2003.031500.[pubmed]
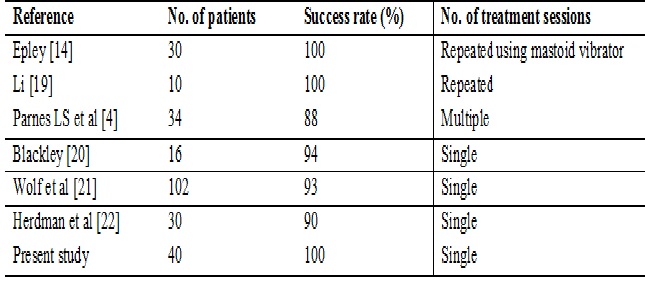
4. Parnes LS, Agrawal SK, Atlas J. Diagnosis and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). CMAJ. 2003 Sep 30;169(7):681-93.[pubmed]
5. Bhattacharyya N, Baugh RF, Orvidas L, et al. Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008 Nov;139(5 Suppl 4):S47-81. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.08.022.[pubmed]
6. Xiang-Dong G. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2011 Jan;2(1):109-10. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.80091.[pubmed]
7. Tang H, Li W. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Sep;14(3):2424-2430. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4837. Epub 2017 Jul 25.[pubmed]
8. Soto Varela A, Bartual Magro J, Santos Pérez S, et al. Benign paroxysmal vertigo: a comparative prospective study of the efficacy of Brandt and Daroff exercises, Semont and Epley maneuver. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2001;122(3):179-83.[pubmed]
9. Davies RA, Luxon LM. Dizziness following head injury: a neuro-otological study. J Neurol. 1995 Mar;242(4):222-30.[pubmed]
10. Gyo K. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo as a complication of postoperative bedrest. Laryngoscope. 1988 Mar;98(3):332-3. DOI:10.1288/00005537-198803000-00019.
11. Marciano E, Marcelli V. Postural restrictions in labyrintholithiasis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2002 May;259(5):262-5. Epub 2002 Mar 19. DOI:10.1007/s00405-001-0445-7.[pubmed]
12. Honrubia V, Baloh RW, Harris MR, et al. Paroxysmal positional vertigo syndrome. Am J Otol. 1999 Jul;20(4):465-70.[pubmed]
13. Soto-Varela A, Santos-Perez S, Rossi-Izquierdo M, et al. Are the three canals equally susceptible to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Audiol Neurootol. 2013;18(5):327-34. doi: 10.1159/000354649. Epub 2013 Sep 28.[pubmed]
14. Epley JM. The canalith repositioning procedure: for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992 Sep;107(3):399-404. DOI:10.1177/019459989210700310
15. Parnes LS, Price-Jones RG. Particle repositioning maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1993 May;102(5):325-31. DOI:10.1177/000348949310200501
16. Lee SH, Kim JS. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Clin Neurol. 2010 Jun;6(2):51-63. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2010.6.2.51. Epub 2010 Jun 30.[pubmed]
17. Prokopakis E, Vlastos IM, Tsagournisakis M, et al. Canalith repositioning procedures among 965 patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Audiol Neurootol. 2013;18(2):83-8. doi: 10.1159/000343579. Epub 2012 Nov 6.[pubmed]
18. Hornibrook J. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): History, Pathophysiology, Office Treatment and Future Directions. Int J Otolaryngol 2011;2011:835671.
19. Li JC. Mastoid oscillation: a critical factor for success in canalith repositioning procedure. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995 Jun;112(6):670-5. DOI:10.1016/S0194-59989570174-5
20. Blakley BW. A randomized, controlled assessment of the canalith repositioning maneuver. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994 Apr;110(4):391-6.[pubmed]
21. Wolf JS, Boyev KP, Manokey BJ, et al. Success of the modified Epley maneuver in treating benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope. 1999 Jun;109(6):900-3.[pubmed]
22. Herdman SJ, Tusa RJ, Zee DS, et al. Single treatment approaches to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993 Apr;119(4):450-4.
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

