Role of Omega-3 fatty acids in meibomian gland dysfunction
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the role of omega-3 fatty acids in meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD).
Design: This was a prospective randomized control study that included patients with MGD attending outpatient Department of Ophthalmology, Subharti Medical College, Meerut.
Subjects: 40 patients of both sex above 40 years of age with MGD were included in the study.
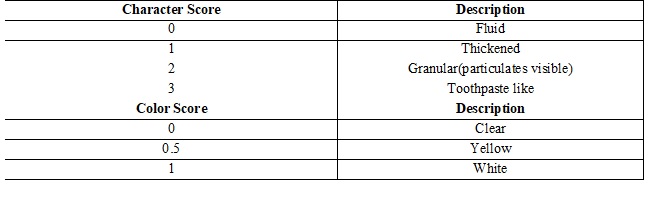
Methods: Age matched randomization of patients was done in two groups of 20 each. Patients in group A were given 2 capsules of 300mg omega-3 fatty acids for 12 weeks while patients in group B were given a placebo oral supplement. Patients were examined at one-month interval for 3 months after the initial visit. At each visit Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI), Schirmer test, Tear film break up time (TBUT), Fluroscein staining and meibum quality score was evaluated.
Results: After 3 months we found statistically significant improvement in subjective as well as objective parameters of group A patients (p value < .05) as compared to group B patients.
Conclusion: Thus, dietary supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids is an effective treatment modality in meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD).
Downloads
References
2. Gilbard JP. Dry eye, blepharitis and chronic eye irritation: divide and conquer. J Ophthalmic Nurs Technol. 1999 May-Jun;18(3):109-15.[pubmed]
3. Nichols KK, Foulks GN, Bron AJ, et al. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: executive summary. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Mar 30;52(4):1922-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6997a.[pubmed]
4. Shimazaki J, Sakata M, Tsubota K. Ocular surface changes and discomfort in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995 Oct;113(10):1266-70.[pubmed]
5. McCulley JP, Shine WE. Meibomian gland function and the tear lipid layer. Ocul Surf. 2003 Jul;1(3):97-106.[pubmed]
6. Shine WE, McCulley JP. Polar lipids in human meibomian gland secretions. Curr Eye Res. 2003 Feb;26(2):89-94.[pubmed]
7. Shine WE, McCulley JP. Role of wax ester fatty alcohols in chronic blepharitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993 Dec;34(13):3515-21.[pubmed]
8. Solomon A, Dursun D, Liu Z, et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory forms of interleukin-1 in the tear fluid and conjunctiva of patients with dry-eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001 Sep;42(10):2283-92.[pubmed]
9. Lam H, Bleiden L, de Paiva CS, et al. Tear cytokine profiles in dysfunctional tear syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009 Feb;147(2):198-205. e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2008.08.032. Epub 2008 Nov 7.[pubmed]
10. James MJ, Gibson RA, Cleland LG. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory mediator production. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Jan;71(1 Suppl):343S-8S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/71.1.343s.[pubmed]
11. Pinna A, Piccinini P, Carta F. Effect of oral linoleic and gamma-linolenic acid on meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2007 Apr;26(3):260-4. DOI:10.1097/ICO.0b013e318033d79b.[pubmed]
12. Schiffman RM, Christianson MD, Jacobsen G, et al. Reliability and validity of the Ocular Surface Disease Index. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000 May;118(5):615-21.[pubmed]
13. Wojtowicz JC, Butovich I, Uchiyama E, et al. Pilot, prospective, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled clinical trial of an omega-3supplement for dry eye. Cornea. 2011 Mar;30(3):308-14. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181f22e03.[pubmed]
14. Oleñik A, Jiménez-Alfaro I, Alejandre-Alba N, Mahillo-Fernández I. A randomized, double-masked study to evaluate the effect of omega-3 fatty acids supplementation in meibomian gland dysfunction. Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8:1133-8. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S48955. Epub 2013 Aug 30.[pubmed]
15. Macsai MS. The role of omega-3 dietary supplementation in blepharitis and meibomian gland dysfunction (an AOS thesis). Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2008;106:336-56.[pubmed]
16. Epitropoulos AT, Donnenfeld ED, Shah ZA, et al. Effect of Oral Re-esterified Omega-3 Nutritional Supplementation on Dry Eyes. Cornea. 2016 Sep;35(9):1185-91. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000940.[pubmed]
17. Opitz DL, Harthan JS, Frometein SR, et al. Diagnosis and management of meibomian gland dysfunction: optometrists’ perspective. Clin Optom.2015; 2015:59-69.
18. Summerton S. Omega-3s: what they can do for you, whether you agree or disagree with the claims, make sure you know the science. Rev Optom.2015;7:32-8.
19. Nagpal H, Rani N, Yadav S, et al. To study the effects of Omega-3fatty acids in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction: A randomized, prospective controlled study. Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences(JDMS).2017;16(10):24-9.
20. Saif AT. Oral linolenic acid dietary supplementation in posterior blepharitis and meibomian gland dysfunction. Delta J Ophthamol.2017;18(2):51-6.
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

