Refractory errors in medical students in a teaching hospital in rural Telangana
Abstract
Introduction: Refractive errors are attributing to major public health problem. The increasing prevalence rates of myopia have reached to epidemic proportions in many Asian countries. Thisstudy was done to determine the prevalence rates of refractive errors in medical students.
Methods: About 350 medical students (aged 19-23 years) of MediCiti Institute of Medical Sciences were examined. Refractive error measurements were determined using an autorefractor. Demographical data was obtained by questionnaires filled in by the students.
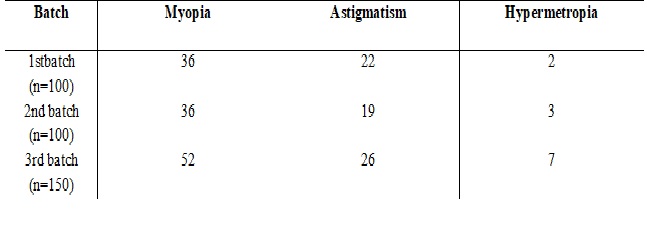
Results: A total of 176 students (40%) of 350 students had refractive errors. A female pre-ponderance was observed. 104 females (59%) and 72 (41%) males. Myopia was seen in 70.45%, Hyperopia was present in 6.8% of the participants and the astigmatism prevalence rate was 38%.
Conclusion: Myopia was the predominant refractive error among the medical students. Hence, timely intervention is the hour of the need as correction of refractive error will increase the productivity thus benefiting the society and the country.
Downloads
References
2. Woo WW, Lim KA, Yang H, et al. Refractive errors in medical students in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2004 Oct;45(10):470-4.[pubmed]
3. Saw SM, Katz J, Schein OD, et al. Epidemiology of myopia. Epidemiol Rev. 1996;18(2):175-87.[pubmed]
4. Teasdale TW, Fuchs J, Goldschmidt E. Degree of myopia in relation to intelligence and educational level. Lancet. 1988 Dec 10;2(8624):1351-4.[pubmed]
5. Shulkin DJ, Bari MM. Deteriorating vision: an occupational risk for the medical student. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986 Sep;104(9):1274.[pubmed]
6. Fledelius HC. Myopia profile in Copenhagen medical students 1996-98. Refractive stability over a century is suggested. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2000 Oct;78(5):501-5.[pubmed]
7. Midelfart A, Aamo B, Sjøhaug KA, Dysthe BE. Myopia among medical students in Norway. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1992 Jun;70(3):317-22.[pubmed]
8. Megbelayin EO. Barriers to uptake of prescribed refractive spectacles amongst Nigerian students. Int. Res.J. Basi Clin. Stud. 2013;1(5):71-77.
9. Chow YC, Dhillon B, Chew PT, Chew SJ. Refractive errors in Singapore medical students. Singapore Med J. 1990 Oct;31(5):472-3.[pubmed]
10. Saw SM, Nieto FJ, Katz J, Chew SJ. Estimating the magnitude of close-up work in school-age children: a comparison of questionnaire and dairy instruments. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 1999; 6:291-301.Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(10) : 474
11. Kinge B, Midelfart A, Jacobsen G, Rystad J. The influence of near-workon development of myopia among university students. A three-year longitudinal study among engineering students in Norway. Acta OphthalmolScand 2000; 78:26-9.
12. Saw SM, Wu HM, Seet B, et al. Academic achievement, close up work parameters, and myopia in Singapore military conscripts. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001 Jul;85(7):855-60.[pubmed]
13. Yap M, Wu M, Liu ZM, et al. Role of heredity in the genesis of myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1993 Jul;13(3):316-9.[pubmed]
14. Chew SJ, Ritch R. Parental history and myopia – taking the long view. JAMA 1994; 272:1255-1256
15. Chaudhry R, Ali H, Sheikh NH. Frequency and underlying factors of myopia among medical students. Biomedica2011;27:154-60.
16. T. Jyothirmai, V. Meenakshi, S.V Padmavathi. A Study on Refractive Errors Among Medical Students Attending Ophthalmology Department.IOSR-JDMS 2017; 16(10): 57-61
17. Onal S, Toker E, Akingol Z, et al. Refractive errors of medical students in Turkey: one year follow-up of refraction and biometry. Optom Vis Sci. 2007 Mar;84(3):175-80. [pubmed
18. Lin LL, Shih YF, Lee YC, et al. Changes in ocular refraction and its components among medical students--a 5-year longitudinal study. Optom Vis Sci. 1996 Jul;73(7):495-8.[pubmed]
19. Wu Y, Yi H, Liu W, Jia H, Eshita Y, Wang S et al. Risk factors for myopia in Inner Mongolia medical students in China. Open Journal of Epidemiology.2012;2: 83-89.
20. Akrami A, Bakmohammad N, Seyedabadi M, Nabipour I, Mirzaei Z, Farrokhi S, et al. The association between schoolchildren intelligence. and refractive error. European Review for Med Pharm Sci.2012;16;908-912.
21. Gopalakrishnan S, Prakash MVS, Kumar Jha KR. A Study of Refractive Errors among Medical students in AIMST University, Malaysia. Indian Med J. 2001;105:365-374.
22. Diether S, Gekeler F, Schaeffel F. Changes in contrast sensitivity induced by defocus and their possible relations to emmetropization in the chicken. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001 Nov;42(12):3072-9.
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

