Effect of donor and host factors on corneal graft transparency
Abstract
Objective: To study the correlation between donor factors and recipients' factors on graft clarity.
Materials and methods: The study comprised 30 cases of Keratoplasty surgery with a follow up of 6 months. All donor corneas were evaluated by Konan specular microscope for endothelial cell count; details of the donor like age, cause of death were noted. The patients were divided into two groups, Group 1 had graft failure, and Group 2 had clear corneas.
Observation and Result: There were 12 patients in group 1 and 18 patients in group 2 with six months of follow up. The mean endothelial cell count in group 1 was 1942.3/mm2, and group 2 was 2334.8/mm2. There is a significant difference in the mean endothelial cell count between the two groups. On analysing the indication for Keratoplasty in two groups, the outcome was best for the corneal opacity group during worst for the graft failure group.
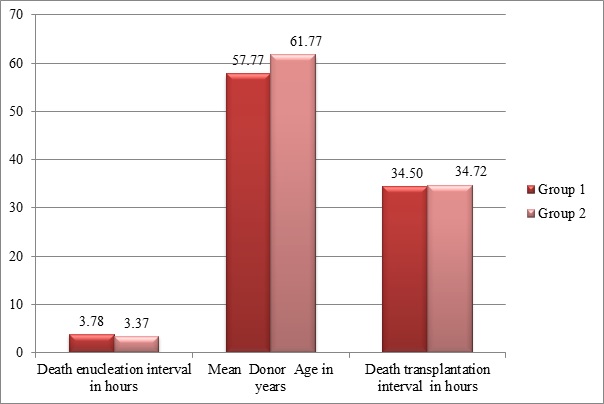
Conclusion: Donor endothelial cell count significantly influenced graft outcome; rest donor factors (age, death enucleation interval, enucleation surgery interval) don't affect graft survival. Indication for Keratoplasty is a significant predictor of graft survival.
Downloads
References
Garg P, Krishna PV, Stratis AK, Gopinathan U. The value of corneal transplantation in reducing blindness. Eye (Lond). 2005 Oct;19(10):1106-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6701968.
Flaxman SR, Bourne RRA, Resnikoff S, Ackland P, Braithwaite T, Cicinelli MV, ET AL. Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990-2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017 Dec;5(12):e1221-e1234. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30393-5.
Verma R, Khanna P, Prinja S, Rajput M, Arora V. The national programme for control of blindness in India. Australas Med J. 2011;4(1):1-3. doi: 10.4066/AMJ.2011.505.
Dandona R, Dandona L. Corneal blindness in a southern Indian population: need for health promotion strategies. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003 Feb;87(2):133-41. doi: 10.1136/bjo.87.2.133.
National Programme for Control of Blindness. Available from: http://pbhealth.gov.in/pdf/Blindness.pdf.
Whitcher JP, Srinivasan M, Upadhyay MP. Corneal blindness: a global perspective. Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79(3):214-21.
Gain P, Jullienne R, He Z, Aldossary M, Acquart S, Cognasse F, Thuret G. Global Survey of Corneal Transplantation and Eye Banking. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016 Feb;134(2):167-73. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.4776.
Hori J. Mechanisms of immune privilege in the anterior segment of the eye: what we learn from corneal transplantation. J Ocul Biol Dis Infor. 2008 Dec;1(2-4):94-100. doi: 10.1007/s12177-008-9010-6.
Niederkorn JY, Mellon J. Anterior chamber-associated immune deviation promotes corneal allograft survival. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996 Dec;37(13):2700-7.
Wu M, Kuang DX, Huang YQ, Miao YR, Liu XC, Dai JJ. Age-related changes of corneal endothelial cell in healthy Chinese tree shrew measured by non-contact specular microscope. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec 18;10(12):1798-1804. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2017.12.02.
Dasar L, Pujar C, Gill KS, Patil M, Salagar M. Indications of penetrating keratoplasty in southern India. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013 Nov;7(11):2505-7. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/7030.3591.
Sony P, Sharma N, Sen S, Vajpayee RB. Indications of penetrating Keratoplasty in northern India. Cornea. 2005 Nov;24(8):989-91. doi: 10.1097/01.ico.0000157406.34662.
Dandona L, Ragu K, Janarthanan M, Naduvilath TJ, Shenoy R, Rao GN. Indications for penetrating Keratoplasty in India. Indian J Ophthalmol. 1997 Sep;45(3):163-8.
The Australian Corneal Graft Registry. 1990 to 1992 report. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol. 1993 May;21(2 Suppl):1-48.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

