Ocular Manifestations Of Carotid Cavernous Fistula and Clinical Outcome After Management
Abstract
Aim: The purpose of the study is to report the ocular manifestations of Carotid cavernous fistula. To confirm the diagnosis by radiological investigations and to evaluate the clinical outcome after management.
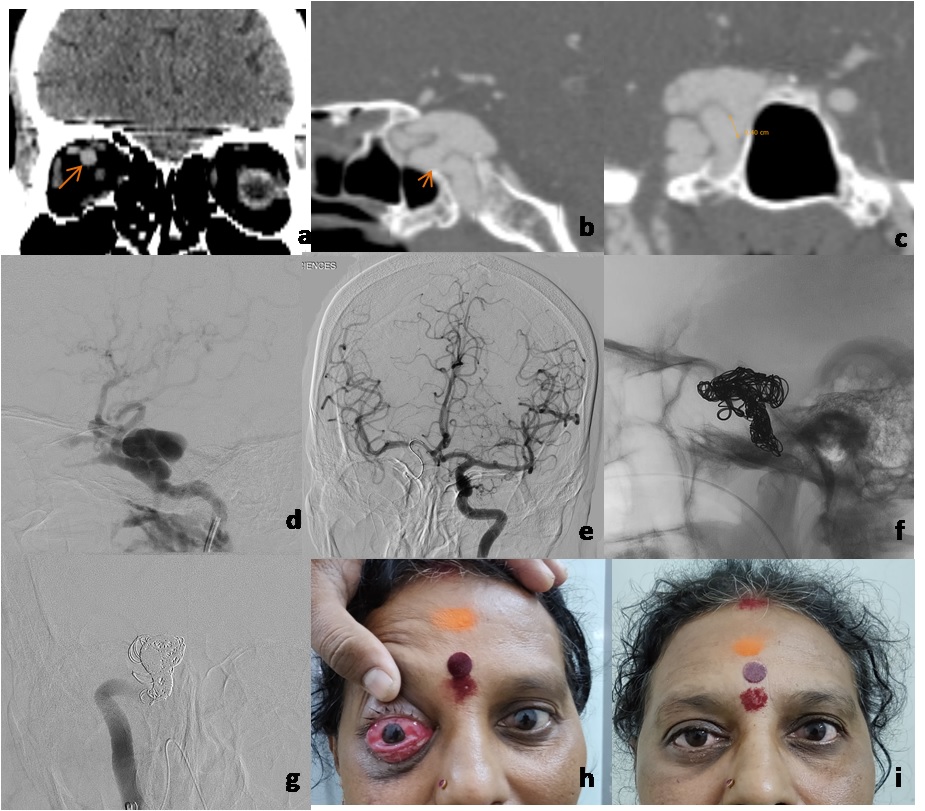
Materials and Methods: Patients who presented to the ophthalmology department with signs and symptoms of carotid-cavernous fistula were evaluated by clinical examination followed by radiological investigations like ultrasound, Doppler, CT scan and MRI. They later underwent DSA ( Digital Subtraction Angiography) for confirmation followed by definitive treatment. Eight cases of CCF were included in the study. Four cases were indirect type and four cases were the direct type of fistulas. Five were females and three were males. The average age was 49years (from 27-69 years).
Results: Out of four patients who had direct CCF, three cases were managed by endovascular embolization of the parent artery. The remaining one case was conservatively managed by carotid massage as it was a low flow fistula and the patient also had Parkinson’s disease. Four cases that had indirect CCF were managed by carotid massage. Complete closure of the fistula is seen in all cases. Patients were followed up for 1 month, 3 months and 6 months and clinical outcome was evaluated. Review scans were done in all the cases to see for complete closure of the fistula. Doppler showed reduced size or calibre of the Superior ophthalmic vein. Follow up Angiogram showed thrombosis of the fistulous communication.
Conclusion: CCF should be suspected in the presence of arteriolised conjunctival vessels, proptosis and audible bruit. Diagnosis is by radiological tests like ultrasonography, Doppler, CT scan and MRI. The confirmatory test is digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Direct CCF is effectively treated with endovascular therapy by coiling the fistula and indirect CCF is managed by manual compression. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent sight-threatening complications.
Downloads
References
Miller, Neil R. "-Diagnosis and management of dural carotid–cavernous sinus fistulas." Neurosurgical Focus 23.5 (2007): E13.
Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, Landman JA, Tindall SC, Tindall GT. Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg. 1985 Feb;62(2):248-56. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.2.0248.
Chi CT, Nguyen D, Duc VT, Chau HH, Son VT. Direct traumatic carotid cavernous fistula: angiographic classification and treatment strategies. Study of 172 cases. Interv Neuroradiol. 2014 Jul-Aug;20(4):461-75. doi: 10.15274/INR-2014-10020.
Das JK, Medhi J, Bhattacharya P, Borah N, Bhattacharjee K, Kuri GC, et al. Clinical spectrum of spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistula. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2007 Jul-Aug;55(4):310-2. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.33051.
Myron Yanoff & Jays.S Duker. Text Book of Ophthalmology. 4th Edition. Elsevier Part 9 Neuro Ophthalmology Section 5 Neuro Ophthalmologic Emergencies & Vascular Disorders. Page No: 993-995.
Chaudhry IA, Elkhamry SM, Al-Rashed W, Bosley TM. Carotid cavernous fistula: ophthalmological implications. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2009 Apr;16(2):57-63. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.53862.
Bhatti MT, Peters KR. A red eye and then a really red eye. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003 Mar-Apr;48(2):224-9. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6257(02)00461-7.
Ishijima K, Kashiwagi K, Nakano K, Shibuya T, Tsumura T, Tsukahara S. Ocular manifestations and prognosis of secondary glaucoma in patients with carotid-cavernous fistula. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2003 Nov-Dec;47(6):603-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jjo.2003.08.002.
de Keizer R. Carotid-cavernous and orbital arteriovenous fistulas: ocular features, diagnostic and hemodynamic considerations in relation to visual impairment and morbidity. Orbit. 2003 Jun;22(2):121-42. doi: 10.1076/orbi.22.2.121.14315.
Preechawat P, Narmkerd P, Jiarakongmun P, Poonyathalang A, Pongpech SM. Dural carotid cavernous sinus fistula: ocular characteristics, endovascular management and clinical outcome. J Med Assoc Thai. 2008 Jun;91(6):852-8.
Lewis AI, Tomsick TA, Tew JM Jr. Management of 100 consecutive direct carotid-cavernous fistulas: results of treatment with detachable balloons. Neurosurgery. 1995 Feb;36(2):239-44; discussion 244-5. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199502000-00001.
Tan AC, Farooqui S, Li X, Tan YL, Cullen J, Lim W, et al. Ocular manifestations and the clinical course of carotid cavernous sinus fistulas in Asian patients. Orbit. 2014 Feb;33(1):45-51. doi: 10.3109/01676830.2013.851253.
Du, Bin, et al. A retrospective analysis of 38 carotid cavernous fistula patients treated with balloon-assisted endovascular fistula embolization through simultaneous transarterial and transvenous approaches." Int J Clin Exp Med 9.10 (2016): 19399-19407.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

