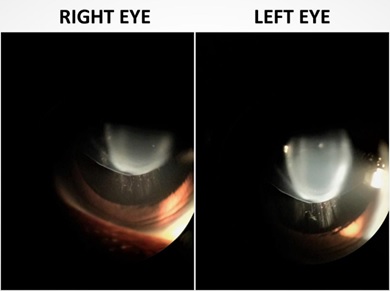
Bilateral subluxation of the lens in a case of sporadic Marfan syndrome
Abstract
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a fibrillin-1 gene mutation (FBN1). Atypical MFS is caused by inactivating mutations in transforming growth factor β receptor (TGFβR). About 30% of cases of MFS do not have a family history.
Downloads
References
Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, Rijlaarsdam ME, Scholte AJ, Berg MS, Versteegh MM, Velzen IS, et al. The clinical spectrum of missense mutations of the first aspartic acid of cbEGF-like domains in fibrillin-1 including a recessive family. Hum Mutat. 2010;31(12):E1915-27. doi:10.1002/humu.21372.
Mizuguchi T, Collod-Beroud G, Akiyama T, Abifodel M, Harada N, Morisaki T, et al. Heterozygous TGFBR2 mutations in Marfan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2004;36(8):855-860. doi:10.1038/ng1392.
Madar L, Szakszon K, Pfliegler G, Szabo GP, Brugos B, Ronen N, et al. FBN1 gene mutations in 26 Hungarian patients with suspected Marfan syndrome or related fibrillinopathies. J Biotechnol. 2019;301:105-111. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2019.05.012.
Waduthantri S. Ocular manifestations of Marfan syndrome. Med J DY Patil Univ 2017;10(2):118-119. doi:10.4103/0975-2870.202118.
Loeys BL, Dietz HC, Braverman AC, Callewaert BL, Backer JD, Devereux RB, et al. The revised Ghent nosology for the Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet. 2010;47(7):476-485. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2009.072785.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

