Effectiveness of Low Vision Aids in patients with low vision attending a medical college hospital
Abstract
Introduction: Low vision is defined as visual impairment despite treatment, surgery, or standard refractive correction, but with the potential to use the residual vision. The aim of the study was to explore the clinical profile of patients requiring Low Vision Aids (LVA) and assess the effectiveness, of LVA among patients with low vision.
Material and Methods: Fifty patients fulfilling the criteria of low vision were recruited after obtaining informed written consent and detailed ocular evaluation was done to detect the cause of low vision. A trial of LVAs was done for near using hand-held magnifiers (+6D, +14D, +20D), stand magnifiers (+8D, +14D, +20D) and spectacle magnifiers (+6D, +10D, +14D, +20D) and visual improvement was noted. Similarly, LVAs were tried for distance using telescope 2.5X and clip-on telescope 3X.
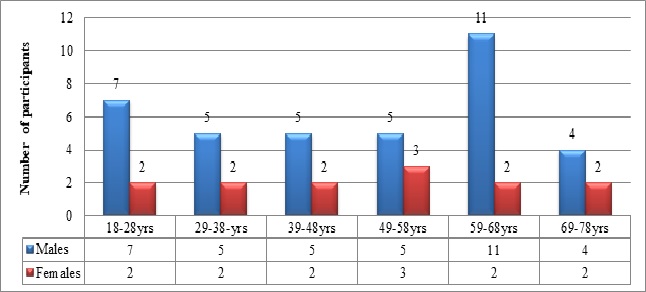
Results: The majority of the participants (72%) belonged to the upper lower class. The most common causes of low vision were heritable conditions like retinitis pigmentosa (24%), bilateral primary optic atrophy (18%), and macular dystrophies (16%). The most effective low vision aids were handheld and stand magnifiers which improved vision by one to four lines. The magnifiers were most effective in eyes with macular dystrophy, retinitis pigmentosa, and age-related macular degeneration.
Conclusion: Low vision aids are potential methods of improving the residual vision in low vision patients. In the background of the high and increasing prevalence of low vision and poor awareness about low vision aids among them, efforts are necessary to rehabilitate them with affordable and accessible low vision services.
Downloads
References
Congdon NG, Friedman DS, Lietman T. Important causes of visual impairment in the world today. JAMA. 2003;290(15):2057‐2060. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.290.15.2057.
Ramke J, Palagyi A, Naduvilath T, du Toit R, Brian G. Prevalence and causes of blindness and low vision in Timor-Leste. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007;91(9):1117‐1121. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2006.106559.
Vijaya L, George R, Asokan R, Velumuri L, Ramesh SV. Prevalence and causes of low vision and blindness in an urban population: The Chennai Glaucoma Study. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2014;62(4):477‐481. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0301-4738.111186.
McCann RM, Jackson AJ, Stevenson M, Dempster M, McElnay JC, Cupples ME. Help needed in medication self-management for people with visual impairment: case-control study. Br J Gen Pract. 2012;62(601):e530‐e537. doi: https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp12X653570.
Dandona R, Dandona L, Srinivas M, Giridhar P, Nutheti R, Rao GN. Planning low vision services in India: a population-based perspective. Ophthalmol. 2002;109(10):1871‐1878. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(02)01183-1.
Li CY, Lin KK, Lin YC, Lee JS. Low vision and methods of rehabilitation: a comparison between the past and present. Chang Gung Med J. 2002;25(3):153‐161.
Jose J, Thomas J, Bhakat P, Krithica S. Awareness, knowledge, and barriers to low vision services among eye care practitioners. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2016;9(1):37‐43. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-620X.176099.
Sarika G, Venugopal D, Sailaja MVS, Evangeline S, Krishna Kumar R. Barriers and enablers to low vision care services in a tertiary eye care hospital: A mixed method study. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67(4):536‐540. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO_1215_18.
Khan SA. A retrospective study of low-vision cases in an Indian tertiary eye-care hospital. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2000;48(3):201‐207.
Margrain TH. Helping blind and partially sighted people to read: the effectiveness of low vision aids. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000;84(8):919‐921. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.84.8.919.
Williams GP, Pathak-Ray V, Austin MW, Lloyd AP, Millington IM, Bennett A. Quality of life and visual rehabilitation: an observational study of low vision in three general practices in West Glamorgan [published correction appears in Eye. 2007 Apr;21(4):575]. Eye (Lond). 2007;21(4):522‐527. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6702256.
Dandona L, Dandona R, Srinivas M, Giridhar P, Vilas K, Prasad MN, et al. Blindness in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42(5):908‐916.
Shetty R, Kulkarni UD. Change-readiness of the blind: a hospital based study in a coastal town of South India. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2014;21(2):158‐164. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-9233.129768.
Carvalho KM, Monteiro GB, Isaac CR, Shiroma LO, Amaral MS. Causes of low vision and use of optical aids in the elderly. Rev Hosp Clin Fac Med Sao Paulo. 2004;59(4):157‐160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/s0041-87812004000400001.
Kulkarni U, Jain R, Savur S, Prabhu V, PD Sowmya, Rasheed R, et al. Perceptions and practices of consanguineous marriage and its implication in the transmission of genetic disorders among the population of South India. JAdv Res Biol Sci. 2010(2):14-18.
Leat SJ, Fryer A, Rumney NJ. Outcome of low vision aid provision: the effectiveness of a low vision clinic. Optom Vis Sci. 1994;71(3):199‐206. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00006324-199403000-00009.
Pollard TL, Simpson JA, Lamoureux EL, Keeffe JE. Barriers to accessing low vision services. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2003;23(4):321‐327. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1475-1313.2003.00123.x.
Dandona R, Dandona L, Srinivas M, Giridhar P, Prasad MN, Vilas K, et al. Moderate visual impairment in India: the Andhra Pradesh Eye Disease Study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002;86(4):373‐377. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.86.4.373.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

