Otogenic abscess: rarity and reality
Abstract
Introduction: Otogenic abscess is a complication commonly arising from active squamous chronic otitis media. It is rare (1:10000) but in fact are a dangerous reality to be managed promptly.
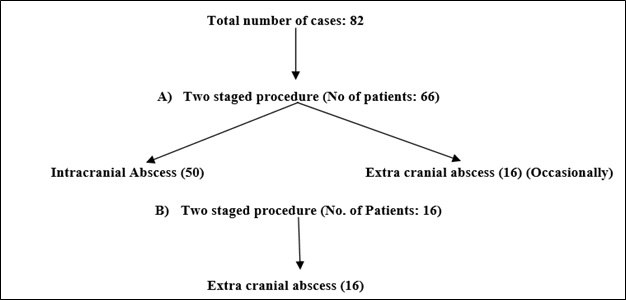
Materials and Methods: A retrospective study of 82 cases of otogenic abscesses were studied over a period 24 years by simple random sampling. Cases of ear malignancy, previously operated mastoidectomy were excluded from study. All postop cases were analysed.
Result: Most commonly affected were male (63.4%) in the second decade (34.1%) of life. Commonest bacterial infection was staphylococcus aureus (31.7%).
Conclusion: Otogenic abscess though rare, are a reality and should be suspected when the patient with chronic ear discharge has high grade fever, severe headache and does not respond to best medical line of treatment. All these patients were subjected to imaging neurosurgical I&D of brain abscess followed by canal wall down tympano-mastoidectomy.
Downloads
References
Browning GG, Merchant SN, Gerad Kelly, Swan LRC, Canter R, McKerrow WS. Chronic otitis media. In: Gleeson M, Browning GG, Burton MJ, Clarke R, Hibbert J, Jones NS, et al (eds). Scott- Brown’s Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. 7th edn. Edward Arnold, Great Britain: 2008: 3395-3445.
Nunez DA, Browning GG. Risks of developing an otogenic intracranial abscess. J Laryngol Otol. 1990;104(6):468-472. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215100112903.
Dubey SP, Larawin V. Complications of chronic suppurative otitis media and their management. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(2):264-267. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000249728.48588.22.
El-Kashlan HK, Harker LA, Shelton C, Aygun N, Niparko JK. Complications of temporal bone infections. In: Flint PW, Haughey BH, Lund VJ, Niparko JK, editors. Cummings Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby-Elsevier; 2010. pp. 1979-1998.
Wanna GB, Dharamsi LM, Moss JR, Bennett ML, Thompson RC, Haynes DS. Contemporary management of intracranial complications of otitis media. Otol Neurotol. 2010;31(1):111-117. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181c2a0a8.
Prasad SC, Shin SH, Russo A, Di Trapani G, Sanna M. Current trends in the management of the complications of chronic otitis media with cholesteatoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;21(5):446-454. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0b013e3283646467.
Thorne MC, Chewaproug L, Elden LM. . Suppurative complications of acute otitis media: changes in frequency over time. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg.2009;135(7):638-641. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/archoto.2009.75.
Syal R, Singh H, Duggal KK. Otogenic brain abscess: management by otologist. J Laryngol Otol. 2006;120(10):837–841. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215106001903.
Laulajainen-Hongisto A, Aarnisalo AA, Lempinen L, Saat R, Markkola A, Leskinen K, Blomstedt G, Jero J; Otogenic Intracranial Abscesses, Our Experience Over the Last Four Decades; Original research, J Int Adv Otol. 2017;13(1):40-46. doi: https://doi.org/10.5152/iao.2016.2758.
Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR, McKhann GM, 2nd, et al. Brain abscess. N Engl J Med2014;371(5):447-456. doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1301635.
Gillanders DA. Gradenigo's syndrome revisited. J Otolaryngol. 1983;12(3):169-174.
Luntz M, Bartal K, Brodsky A, Shihada R. Acute mastoiditis: the role of imaging for identifying intracranial complications. Laryngoscope. 2012;122:2813-2817 doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.22193. Epub 2012 Sep 7.
Prashanth V, Pandya VK. Role of CT Scan in Diagnosis and Management of Otogenic Intracranial Abscess. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;63(3):274-278. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0255-1. Epub 2011.
Grewal DS, Mistry B, Gaikwad N. Otogenic abscesses—our experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995;47(2):106-112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03047937.
Szyfter W, Kruk-Zagajewska A, Borucki L, Bartochowska A. Evolution in management of otogenic brain abscess. Otol Neurotol. 2012;33(3):393-395. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e3182488007.
Brook I. The role of anaerobic bacteria in chronic suppurative otitis media in children: implications for medical therapy. Anaerobe 2008;14(6):297-300. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2008.12.002. Epub 2008 Dec 16.
Raja K, Parida PK, Alexander A, Surianarayanan G. Otogenic Lateral Sinus Thrombosis: A Review of Fifteen Patients and Changing Trends in the Management. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018;22(3):208-213. doi: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1604198. Epub 2017 Jul 14.
Alho OP, Jokinen K, Laitakari K, Palokangas J (1997) Chronic suppurative otitismedia and cholesteatoma. Vanishing diseases among Western populations. Clin Otolarynol 1997;22(4):358-361. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2273.1997.00027.x.
de Oliveira Penido N, Testa J R, Inoue D P, Cruz O L. Presentation, treatment, and clinical course of otogenic lateral sinus thrombosis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009;129(07):729–734. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480802399721.
Bradley D.T., Hashisaki G.T., Mason J.C. Otogenic Sigmoid Sinus Thrombosis: What Is the Role of Anticoagulation? The Laryngoscope.2002;112(10):1726-1729. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200210000-00003.
Osma U, Cureoglu S, Hosoglu S. The complications of chronic otitis media: Report of 93 cases. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2000;114(2):97-100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1258/0022215001905012.
Smith JA, Danner CJ. Complications of chronic otitis media and cholesteatoma. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006;39(6):1237–1255. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2006.09.001.
Palva T, Johnsson LG. Preservation of hearing after removal of the membranous canal with cholesteatoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986;122(9):982-985. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1986.03780090078015.
Chiossone E. Labyrinthine fistulae in cholesteatoma. Adv Otorhinolaryngol: In Otology Today. 1987;37:128-133. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000414125.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative



















 Therapoid
Therapoid

