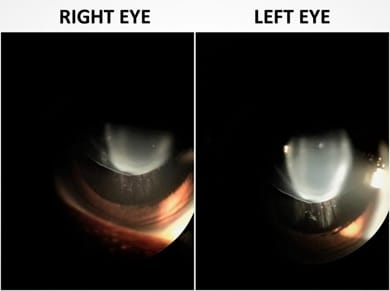
Bilateral subluxation of the lens in a case of sporadic Marfan syndrome
Senthamizh T.1*, Mani M.2, Babu R.3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/jooo.2020.i07.01
1* Tharini Senthamizh, Senior Resident, Department of Ophthalmology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India.
2 Malavika Mani, Senior Resident, Department of Ophthalmology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India.
3 Ramesh Babu, Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India.
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a fibrillin-1 gene mutation (FBN1). Atypical MFS is caused by inactivating mutations in transforming growth factor β receptor (TGFβR). About 30% of cases of MFS do not have a family history. These sporadic cases occur due to de novo gene mutations. We report a case of a 16-year-old female, who presented with progressive diminution of vision in both the eyes for the past 5 years. On ocular examination, her right eye visual acuity was 5/60 and left eye visual acuity was 6/60, with a clear cornea.
Keywords: Sporadic, Lens Subluxation, Marfan Syndrome,
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Senior Resident, Department of Ophthalmology, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India. Email: |
Senthamizh T, Mani M, Babu R. Bilateral subluxation of the lens in a case of sporadic Marfan syndrome. Trop J Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 2020;5(7):172-173. Available From https://opthalmology.medresearch.in/index.php/jooo/article/view/161 |


 ©
©